McCune-Albright syndrome
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
McCune-Albright syndrome is a genetic disease that affects the bones, hormones, and color (pigmentation) of the skin.
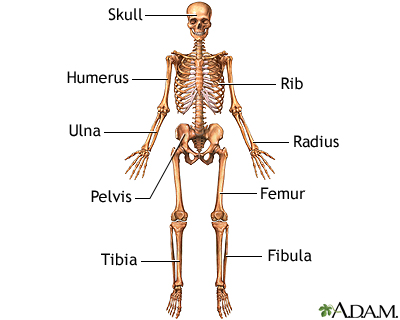
The skeleton is made up of 206 bones in the adult and contributes to the form and shape of the body. The skeleton has several important functions for the body. The bones of the skeleton provide support for the soft tissues. For example, the rib cage supports the thoracic wall. Most muscles of the body are attached to bones which act as levers to allow movement of body parts. The bones of the skeleton also serve as a reservoir for minerals, such as calcium and phosphate. Finally, most of the blood cell formation takes places within the marrow of certain bones.
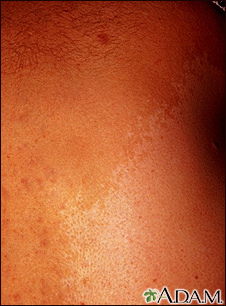
People with neurofibromatosis often have more than 6 light brown spots -- cafe-au-lait spots -- larger than 1.5 centimeters. This is a picture of a giant cafe-au-lait spot on a person with neurofibromatosis.
Causes
McCune-Albright syndrome is caused by changes in the GNAS gene. A small number, but not all, of the person's cells contain this faulty gene (mosaicism).
This disease is not inherited.
Symptoms
The main symptom of McCune-Albright syndrome is early puberty in girls. Menstrual periods may begin in early childhood, long before the breasts or pubic hair develop (which normally occur first). The average age that symptoms appear is 3 years old. However, puberty and menstrual bleeding have occurred as early as 4 to 6 months in girls.
Early sexual development may also occur in boys, but not as often as in girls.
Other symptoms include:
- Bone fractures
- Deformities of the bones in the face
- Gigantism
- Irregular, large patchy café au lait spots
Exams and Tests
A physical examination may show signs of:
- Abnormal bone growth in the skull
- Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Acromegaly
- Gigantism
- Large cafe-au-lait spots on the skin
- Liver disease, jaundice, fatty liver
- Scar-like tissue in the bone (fibrous dysplasia)
Tests may show:
- Adrenal abnormalities
- High level of parathyroid hormone (hyperparathyroidism)
- High level of thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism)
- Adrenal hormone abnormalities
- Low level of phosphorous in the blood (hypophosphatemia)
- Ovarian cysts
- Pituitary or thyroid tumors
- Abnormal blood prolactin level
- Abnormal growth hormone level
Other tests that may be done include:
- MRI of the head
- X-rays of the bones
Genetic testing may be done to identify the gene variant responsible for the symptoms.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for McCune-Albright syndrome. Medicines that block estrogen production, such as testolactone, have been tried with some success.
Adrenal abnormalities (such as Cushing syndrome) may be treated with surgery to remove the adrenal glands. Gigantism and pituitary adenoma will need to be treated with medicines that block hormone production, or with surgery.
Bone abnormalities (fibrous dysplasia) are sometimes removed with surgery.
Limit the number of x-rays taken of affected areas of the body.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Lifespan is relatively normal.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Blindness
- Cosmetic problems from bone abnormalities
- Deafness
- Osteitis fibrosa cystica
- Premature puberty
- Repeated broken bones
- Tumors of the bone (rare)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if your child starts puberty early, or has other symptoms of McCune-Albright syndrome. Genetic counseling, and possibly genetic testing, may be suggested if the disease is detected.
References
Garibaldi LR, Chemaitilly W. Disorders of pubertal development. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 600.
Styne DM. Physiology and disorders of puberty. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Rosen CJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 26.
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 8/18/2024
Reviewed by: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
